Research Areas
Women’s Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation (WISE) Coronary Vascular Dysfunction
This WISE study is investigating detection and assessment of heart artery disorders in women using noninvasive methods that don’t break the skin or physically enter the body. The results of these methods are compared with results of standard care invasive diagnostic procedures, which involve tools that break the skin or physically enter the body, including angiogram, as well as with the results of an additional noninvasive diagnostic procedure, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging.
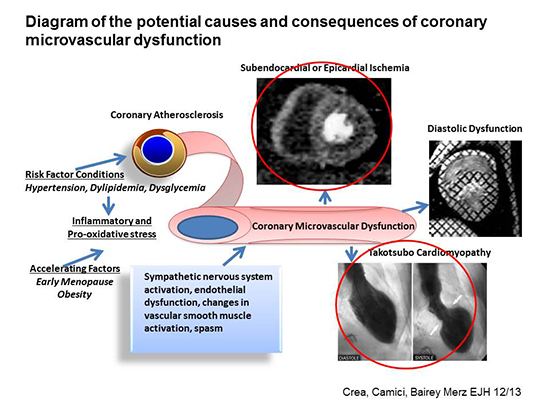
Women's Ischemia Syndrome Evaluation (WISE) - Mechanisms of Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction Leading to Pre-Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF)
Treatment with Ranolazine in Microvascular Coronary Dysfunction (MCD): Impact on Angina and Myocardial Ischemia
The ranolazine study is designed to test the use of this drug in patients with angina (chest discomfort due to reduced blood supply to the heart) caused by MCD (abnormalities in the small blood vessels of the heart). Ranolazine is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of chronic angina. The FDA has approved this drug based on studies primarily on patients with chronic angina with major blockages of the arteries. This drug has not been systematically studied in the subset of patients who have angina with MCD.
A Noninvasive Index of the Detrimental Cardiopulmonary Effects of Secondhand Smoke
This research study is designed to test whether exposure to secondhand tobacco smoke causes negative health effects. In particular, the investigators wish to find out whether secondhand tobacco smoke exposure causes heart or lung problems.
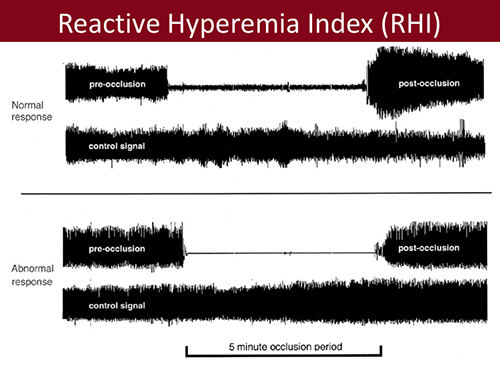
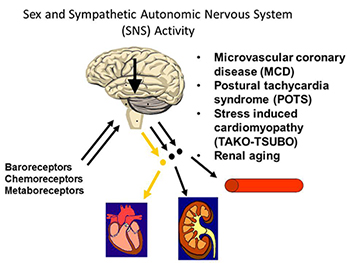
Cardiac Autonomic Function In Women with Microvascular Coronary Dysfunction (MCD)
MCD occurs when abnormities in small blood vessels/arteries in the heart cause symptoms of persistent chest pain that affect women. An estimated 2 to 3 million women in the U.S. have MCD, and about 100,000 new cases are diagnosed annually. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is part of the central nervous system and helps the body adapt to changes in the environment. ANS normally controls involuntary activities, such as heart rate, respiration, body temperature, blood pressure and urinary function. However, there is a limited understanding of the role of the heart’s ANS in women who have MCD. The purpose of this research is to investigate how the heart reacts to mental stress and to understand more about the cardiac nervous system in women with MCD.
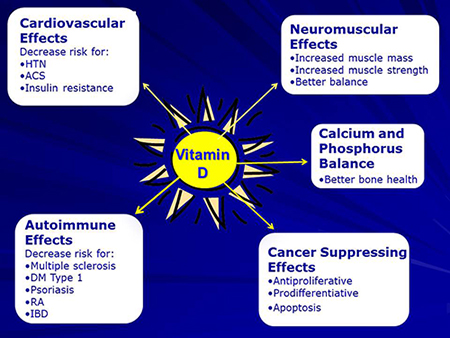
Is Treatment of Vitamin D Deficiency Associated with Resolution of Statin-Induced Muscular Symptoms?
This study is testing whether treatment with Vitamin D can alleviate statin-induced muscle pain in subjects with Vitamin D deficiency. If Vitamin D treatment is effective, it will provide patients a low-cost, low-risk intervention that would enhance statin compliance. Statins are a class of drugs that are highly effective at lowering cholesterol levels. However, compliance is often limited by side effects of muscle pain. When a patient experiences muscle pain from a statin treatment, the current standard of care is to attempt a different statin medication. This study examines Vitamin D-deficient individuals who also have muscle pain caused by statin use. About 1 billion people are estimated to have low or insufficient levels of vitamin D worldwide. Patients with low or insufficient levels of Vitamin D are at risk to develop muscle disease.
Estrogen Deficiency and Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) in Premenopausal Women
Premature CVD is the leading cause of death in young women; yet, traditional risk factors underestimate CVD risk. To date, there has been no study assessing the relationship between the abnormal absence of menstruation or functional hypothalamic amenorrhea (FHA), CVD risk factors and subclinical CVD. In this pilot study, we hope to find out whether FHA in young women is associated with CVD risk factors, and whether FHA is a sign of early-stage CVD.
Contact the Bairey Merz Lab
127 S. San Vicente Blvd.
Pavilion, A9300
Los Angeles, CA 90048