Research Areas
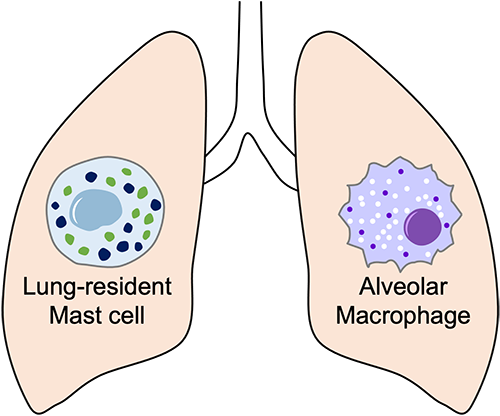
Our objective is to establish an interdisciplinary program delving into innate immune response in the respiratory system. We are understanding how these responses influence allergic and inflammatory lung diseases, with a specific focus on the biochemistry, cell biology and immunology of lung-resident mast cells and alveolar macrophages. By leveraging mechanistic findings, we are developing novel therapeutic strategies for conditions such as asthma and lung fibrosis.
Current Research Projects
Lung Mast Cell-Specific Innate Immune Responses in Chronic Asthma
Our investigation of the mechanisms governing the immune system in asthma discovered the pivotal role of MCEMP1 in KIT receptor signaling, driving mast cell proliferation. Through in-depth in vivo studies, we linked MCEMP1 to severe asthma, identifying it as a crucial adaptor promoting SCF-mediated mast cell proliferation. Future research will delve into MCEMP1's mast cell-specific function, its relationship with KIT activity, and its implications for asthma severity. Understanding these mechanisms could inform therapeutic strategies to reduce airway mast cell burdens in severe asthma.
Alveolar Macrophage-Specific Innate Immune Responses in Pulmonary Fibrosis
Focusing on alveolar macrophages as major profibrotic mediators, our research centers on MCEMP1-mediated inhibitory signaling pathways and its role in lung fibrosis. We are developing a conditional macrophage-specific MCEMP1 knockout mice to explore MCEMP1's function in distinct immune cell types during lung fibrosis development. Employing diverse techniques (including flexiVent, flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry and single-cell RNA sequencing), this research aims to deepen our understanding of MCEMP1's macrophage cell-specific role in pulmonary fibrosis.

Therapeutic Inhibitors for Treating Inflammatory Lung Diseases
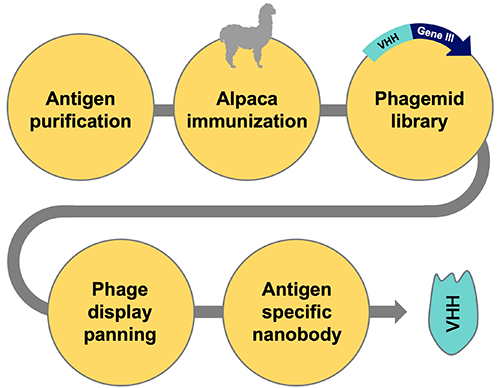
MCEMP1 is a transmembrane protein that is upregulated in many allergic and inflammatory lung diseases, making it a compelling therapeutic target. We are developing MCEMP1 inhibitors using two strategies: Fc-fusion (Fc-MCEMP1 fusion) for enhanced stability and therapeutic efficacy, and nanobodies targeting MCEMP1's extracellular region for versatility in expression and screening. Both strategies will offer broad applications in therapeutics, diagnostics, and research tools.
Contact the Choi Lab
121 North San Vicente Boulevard, Room 211
Beverly Hills, CA 90211
